With AWS Systems Manager, you can gain operational insights into your AWS and on-premises resources, so you can improve the reliability of your IT infrastructure while reducing the cost of operation and increasing the speed of innovation. This blog post will introduce you to the key features of AWS Systems Manager and how you can use it to help simplify your IT management, helping save time and money in your day-to-day operations
Why Amazon Web Services?
If you have questions about integrating AWS with on-premises systems, you aren’t alone. Many organizations are overwhelmed by all of their cloud options—you’ve got to choose among more than 300 service offerings. The good news is that you can integrate those services, even if they come from different vendors. AWS Systems Manager (SSM) offers an automated solution for provisioning, monitoring, configuring, and updating IT infrastructure elements in your hybrid cloud deployments.
How does it work?
AWS Systems Manager uses AWS Cloud Formation to create a set of resources, including EC2 instances and IAM roles. The service can automatically provision and update resources by using configurations that you define.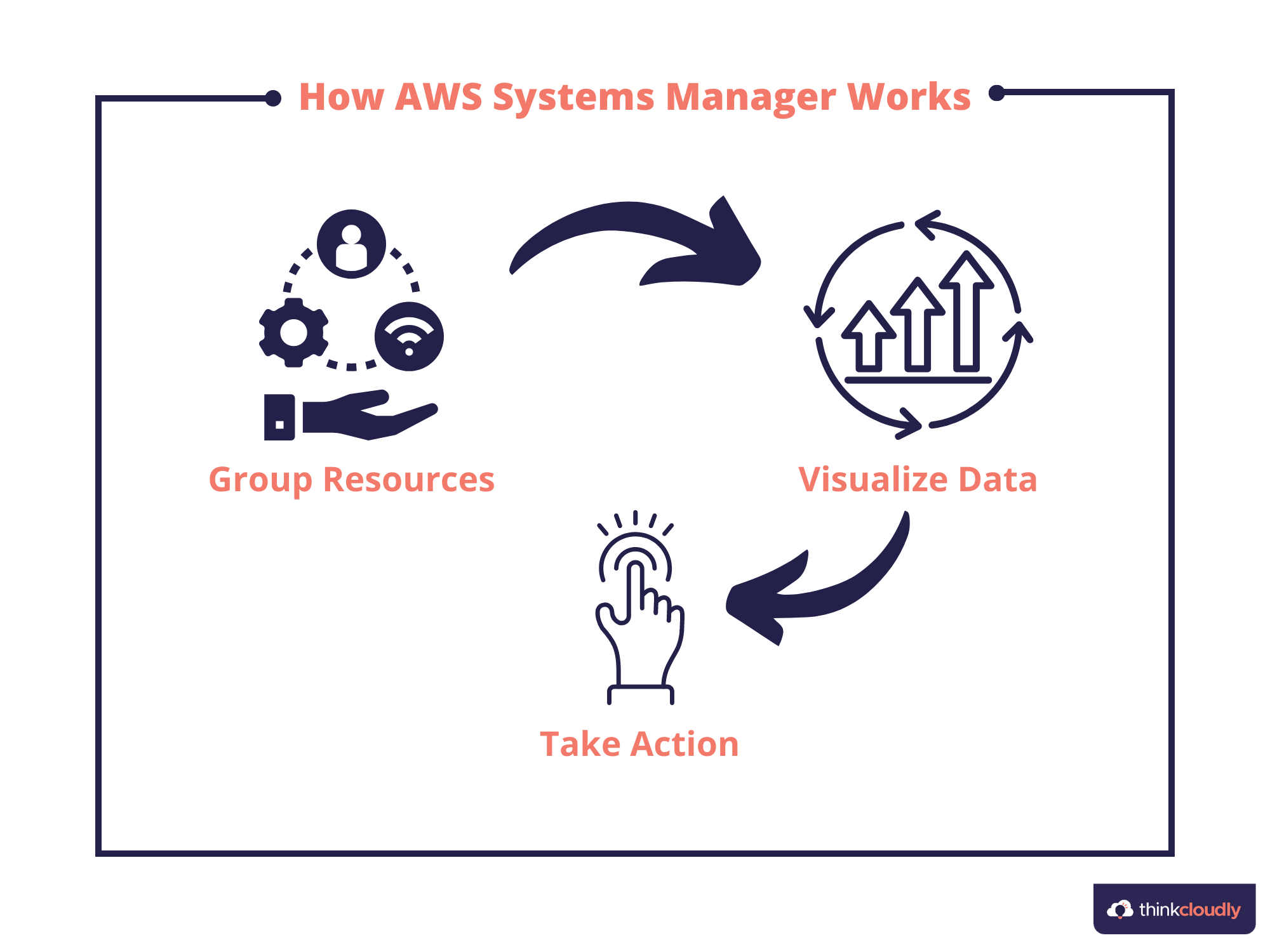
AWS systems manager Features:
- Define policies that automate the management of AWS resources
- Gain operational insights by monitoring services, security, and configuration compliance across your AWS accounts, VPCs, or individual instances.
- Enable Amazon GuardDuty to continuously monitor for threats using built-in security intelligence from Amazon Web Services.
Benefits of using Amazon Systems Manager:
System management is a time-consuming task. If you have multiple systems to manage, it can be challenging to ensure they’re all up-to-date and functioning properly. Rather than keeping track of these systems manually, Amazon System Manager (ASM) takes over the process and automates it. In addition to patching systems automatically, ASM also collects application configuration data (inventory) so you have a complete view of what’s installed across all your systems.
Build Your Career as a
AWS Solution Architect
- Live Projects
- Resume / Interview Preparation

7 Tips to Get the Best Out of AWS Systems Manager:
A major benefit of running your applications in the cloud with AWS is being able to quickly and easily scale resources up or down as needed to accommodate changing workloads. With AWS Systems Manager, it’s possible to remotely manage your AWS resources, including creating policies and workflows to automate recurring management tasks, while also gaining insights into on-premises resources that are managed by the Systems Manager. If you aren’t familiar with this service yet, here are seven tips that will help you get the most out of AWS Systems Manager.
1) Link Syslog Transport for CloudWatch:
If you’re managing workloads that use AWS resources but don’t run in EC2, AWS Systems Manager provides a lightweight mechanism for delivering log data to CloudWatch Logs and CloudWatch Events. As with other log sources, you can view data via CloudWatch dashboards or Kibana. This functionality is supported on Linux using Rsyslog or Syslog-ng and requires Network Time Protocol (NTP) as well as secure TCP connections.
2) Connect Amazon VPC Flow Logs to CloudWatch Logs:
Learn how you can use AWS Systems Manager policies to automatically collect flow data from your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) and forward it to CloudWatch Logs for further analysis. Learn how you can leverage CloudWatch Logs to run alerting and log analysis, develop customized dashboards, and gain operational insights about your AWS infrastructure and on-premises resources connected via VPN or Direct Connect. You’ll also learn how you can analyze traffic patterns in your VPC by leveraging IP flow information.
3) Use Predefined AWS Systems Manager Templates:
AWS Systems Manager enables you to automatically discover and manage on-premises servers and AWS resources. It can also gather data from on-premises Windows servers using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) sensors and send it to Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring. You can use predefined templates for common IT management tasks, such as patching operating systems, starting or stopping instances, or configuring network settings.
4) Integrate with CloudTrail, CloudWatch Events, and Amazon GuardDuty:
If you’re responsible for running any part of AWS, AWS Systems Manager is one tool you need to become familiar with. It allows you to manage many aspects and features of your AWS resources, including logging and auditing. Integrating CloudTrail, CloudWatch Events, and Amazon GuardDuty with AWS Systems Manager gives you better visibility into what’s happening across your account—especially if someone on your team makes a mistake or creates an instance that isn’t secure.
5) Configure Remediation Actions with Lambda
AWS Systems Manager (SSM) is a service that helps you manage your IT infrastructure in AWS and on-premises, using policy-based automation. One of SSM’s key features is its ability to monitor resources and proactively correct any issues that arise by using Lambda functions.
Boost your earning potential with AWS expertise. Explore our certified AWS Courses for a high-paying career
6) Use the Redshift Spectrum Migration Tool:
If you’re moving data from an on-premises database into AWS, the Redshift Spectrum Migration Tool can automate that process. The tool, available via AWS Systems Manager (SSM), lets you migrate on-premises data into an Amazon Redshift cluster with minimal IT intervention.
7) Create EBS Snapshots from EC2 Instances in Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) using EC2 Run Command:
The AWS Systems Manager service is designed for system administrators and IT operations teams to gain operational insights into AWS and on-premises resources. In particular, it gives you insights into your infrastructure services, such as Amazon EC2, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), and Autoscaling. You can use AWS Systems Manager with other AWS services, including Amazon S3 and Amazon CloudWatch, allowing you to fully automate provisioning tasks.
Conclusion:
AWS Systems Manager (SSM) provides you with a centralized console for managing all of your AWS resources. It also lets you gather operational data from servers, application components, and other IT infrastructure that run in Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). You can use SSM to track configuration changes and configurations in real time. SSM helps you gain deeper visibility into existing cloud environments, reduce risk, increase control over applications, simplify compliance processes, and improve performance.
See you in the next blog till then browse our blogs on cloud computing Certification. Happily Thinkcloudly!










